Seam Welder
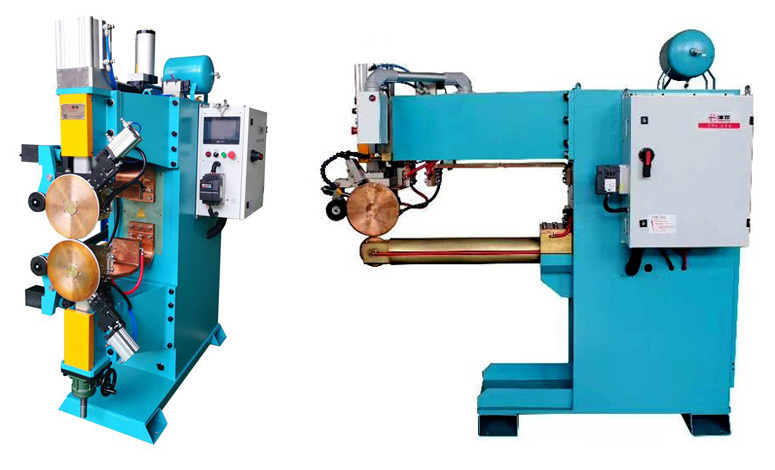
 Seam welding operates under the principle of coalescence, uniting two metal sheets or workpieces through a series of overlapping spot welds.
Seam welding operates under the principle of coalescence, uniting two metal sheets or workpieces through a series of overlapping spot welds.
The welding process in which two similar or dissimilar materials are joined at the seam by the application of heat generated from electrical resistance. The seam welding is a types of resistance welding, in which weld is produced by roller electrodes instead of tipped electrodes.
Most seam welding processes produce a continuous or intermittent seam weld near the edge of two overlapped metals by using two machine driven roller electrodes. As in the seam welding process, the roller electrodes move over the metal workpieces, the workpieces are under pressure and the current passing through them heats the two workpieces of the metal to the melting point. Thus, this process, sometimes, also called the seam spot welding.
The resistance seam welding is broadly classified into two types,
Intermittent Seam Welding – In case of intermittent welding, the weld occurs at specific spots rather than as a continuous line. This type of seam welding is useful for welding thick metals where a continuous weld is not possible.
Continuous Seam Welding – In continuous seam welding, an uninterrupted current flows through the electrodes and the metals to be joined are passed through the electrodes at a constant speed. As the workpieces remain under constant pressure, thus, it produces a uniform overlapping weld. Continuous seams are long, uninterrupted welds ideal for liquid-tight joints. Intermittent or stitch welding leaves gaps and is commonly used in applications that don’t require a hermetic seal.
The choice often hinges on the project’s requisite integrity level for the joined materials.
Seam welder features abd advantages
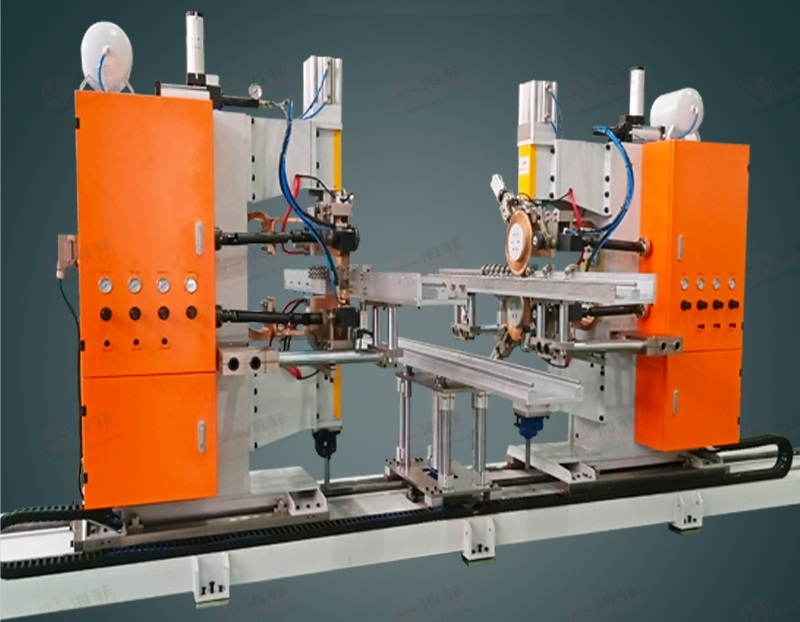 1. Seam welder can be automated using robotic machines.
1. Seam welder can be automated using robotic machines.
2. No need of any flux and filler materials.
3. High welding speeds, a high degree of automation, making it ideal for high-volume production runs.
4. Excellent weld consistency and quality due to seam welder produces minimal distortion of the materials being joined.
5. Compared to other welding techniques, seam welder produces less heat input, resulting in less distortion, warping, and residual stress in the materials being joined..
Weldable metals
Iron, carbon steel, stainless steel, galvanized steel, copper, brass, aluminium, nickel, tin, alloy, etc
Industries
Automotive, Aerospace, Architecture and Construction, Food and Beverage Packaging, Kitchenware, Hardware, etc.
Manufacturing and Repairing
Welded products
Get a quote
Specification and parameters
AC Seam Welder
|
|
Items \ Model |
unit |
FN-100H |
FN-160H |
FN-200H |
|
1 |
Rated capacity |
KVA |
100 |
160 |
200 |
|
2 |
Power supply |
V/Ø/Hz |
380V±10% / 3 phases / 50Hz |
||
|
3 |
Rated duty cycle |
% |
50% |
50% |
50% |
|
4 |
Secondary voltage no load |
V |
5.94 - 7.6 |
5.94 - 9.04 |
9.04 - 10 |
|
5 |
Welding thickness |
mm |
1.2+1.2 |
1.8+1.8 |
2+2 |
|
6 |
Electrode force Max. |
KN |
7 |
8 |
10 |
|
7 |
Cylinder stroke |
mm |
100 |
130 |
105 |
|
8 |
Cooling water consumption |
L/h |
1200 |
1500 |
2050 |
|
9 |
Working environment |
|
temperature: 1~45℃ humidity: 35~90% |
||
DC Seam Welder
|
|
Items \ Model |
unit |
FN-100HB |
FN-160HB |
FN-200HB |
|
1 |
Rated capacity |
KVA |
100 |
160 |
200 |
|
2 |
Power supply |
V/Ø/Hz |
380V±10% / 3 phases / 50Hz |
||
|
3 |
Rated duty cycle |
% |
50% |
50% |
50% |
|
4 |
Secondary voltage no load |
V |
3.52 - 7.04 |
4.52 - 9.05 |
10.6 - 12.67 |
|
5 |
Welding thickness |
mm |
1.2+1.2 steel |
1.8+1.8 steel |
2+2 steel |
|
6 |
Electrode force Max. |
KN |
10 |
10 |
10 |
|
7 |
Cylinder stroke |
mm |
100 |
100 |
100 |
|
8 |
Cooling water consumption |
L/h |
1440 |
1800 |
2460 |
|
9 |
Working environment |
|
temperature: 1~45℃ humidity: 35~90% |
||
Key words:
Seam Welder
More Content
Get a Free Product Quote
If you are interested in our products, please leave your contact information and we will dispatch experts to communicate with you within 24 hours.

 Language
Language


